How does it work?
The main component of DC MOTOR 14 click is the TB67H450FNG, a PWM chopper-type brushed DC motor driver, produced by Toshiba. This IC uses a proprietary BiCD manufacturing process, allowing this IC to be powered by a wide range of supply voltages, from 4.5 up to 44V. Due to a very low ON resistance of the MOSFETs, it can theoretically deliver up to 3.5A (Peak current is 6.2A (tw<=500ns)) of current to the connected load. However, many external parameters affect both the maximum voltage and the current specifications, especially when the connected load is of a complex nature, such as the DC motor. In using TB67H450FNG, the voltage should be applied to the pins of VM and VREF. The absolute maximum rating of VM supply voltage is 50V (no active). The usage range is 4.5 to 44V. The absolute maximum rating of VREF supply voltage is 5V. The usage range is 0 to 4V.
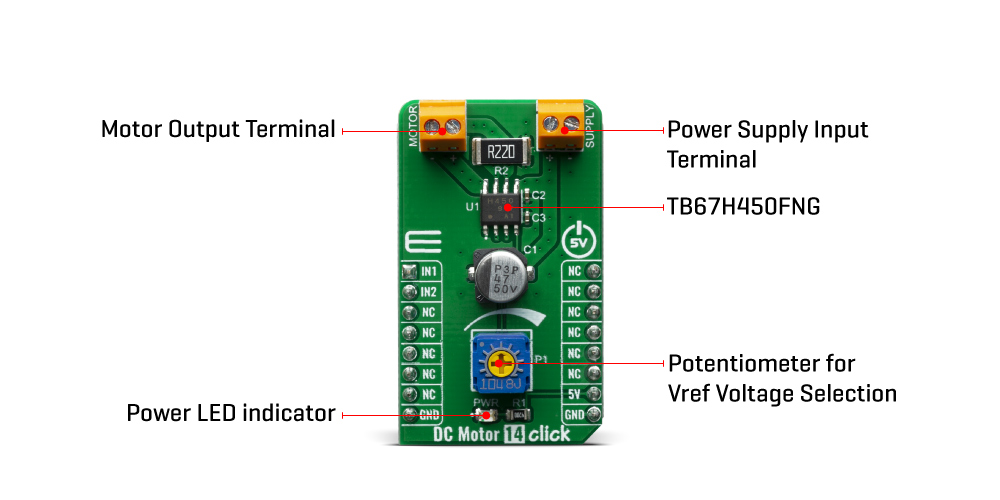
There are no special procedures of inputting a power supply and shutdown because the TB67H450FNG incorporates the under voltage lockout (UVLO). However, under the unstable state of inputting the power supply (VM) and shutdown (transient area), setting the motor operation to OFF state is recommended. After the power supply is in the stable state, the motor should be operated by switching the input signal.The absolute maximum rating of motor output current is 3.5A (Peak current is 6.2A (tw<=500ns)). Its operating range is 3A or less. The maximum current of the actual usage is limited depending on the usage conditions (the ambient temperature, the wiring pattern of the board, the radiation path, and the exciting design). Configure the most appropriate current value after calculating the heat and evaluating the board under the operating environment.
When the logic signal is input under the condition that the voltage of VM is not supplied, the electromotive force by an input signal is not generated. However, configure the input signal low level before the power supply is applied by referring to the detailed description in datasheet (???1.2 Power Supply Sequence???).
A speed of the motor can be controlled by Inputting PWM signal to pins IN1 and IN2, and operating them with PWM control.When both IN1 and IN2 pins are set to L for 1 ms (typ.) or more, the operation mode enters into the standby mode. When IN1 or IN2 is set to H, the mode returns from the standby mode, and enters to the operation mode.
When the constant current function is disabled, RS pin should be connected to GND, and the voltage of 1 to 5V should be applied to VREF pin. Maximum 30 ??s are required for the return time from the standby release. The OUT1 and OUT2 outputs operate after 30 ??s (max) from the standby release.
In this product, a constant current threshold is set by the current detection resistor between RS and GND, and VREF input voltage. When the constant current function is disabled, RS pin should be connected to GND, and the voltage of 1 to 5V should be applied to VREF pin. When the output current reaches the threshold due to forward rotation and reverse rotation, the constant current control is performed in Mixed Decay mode. In case of the constant current control, the OFF time (toff) is fixed to 25 ??s (typ.) to determine the pulse width of the current (current pulsating flow). The percentage of Mixed Decay Mode is as follows; Fast Mode: 50% to Slow Mode: 50%. If the output current is zero-detected in Fast Mode, the outputs are in High impedance.
When the junction temperature of the IC reaches the specified value, the internal detection circuit (TSD) operates to turn off the output block. It has a dead band time to prevent the IC from malfunction, which is caused by switching and so on. Since the temperature has a hysteresis range, when the junction temperature falls to the return temperature, the operation returns automatically to the normal operation.
The TSD is triggered when the device is over heated irregularly. Make sure not to use the TSD function aggressively. When the IC detects an over current, the internal circuit turns off the output block. It has a dead band time to avoid ISD misdetection, which may be triggered by external noise. The under voltage detection circuit operates when the applied voltage of VM pin falls 3.8V (typ.) or less. All output power transistors are turned off. The UVLO operation is released when the voltage applied to VM pin rises 4.0V (typ.) or more.
Although the TB67H450FNG IC requires an external PSU, The Click board™ can operate with 5V MCUs only. The current detection resistor (R2) installed on click is 0.51 ohm and set for range from 0 to 1.5A. If it's needed range from 1.5 to 3A, that can be achieved by replacing it with 0.22 ohm resistor. It is ready to be used as soon as it is inserted into a mikroBUS™ socket of the development system.
Specifications
| Type |
Brushed |
| Applications |
Usable for various RC cars and boats, small to medium-sized robots, drones, and similar applications. as well as for driving motors in air or water pumps, air conditioners, ventilation systems, handheld tools, etc. |
| On-board modules |
DC MOTOR 14 click is a PWM chopper type brushed DC motor driver, labeled as TB67H450FNG. This IC includes one channel of motor output block, using a wide range of supply voltages, while delivering reasonably high current to the connected DC motors. |
| Key Features |
Complete DC brushed motor driving solution with reasonably high current capability, a wide range of power supply voltages supported |
| Interface |
GPIO |
| Compatibility |
mikroBUS |
| Click board size |
M (42.9 x 25.4 mm) |
| Input Voltage |
5V |
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on DC Motor 14 Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
| Notes |
Pin |
 |
Pin |
Notes |
|---|
| Ctrl IN1 |
IN1 |
1 |
AN |
PWM |
16 |
NC |
|
| Ctrl IN2 |
IN2 |
2 |
RST |
INT |
15 |
NC |
|
| |
NC |
3 |
CS |
RX |
14 |
NC |
|
| |
NC |
4 |
SCK |
TX |
13 |
NC |
|
| |
NC |
5 |
MISO |
SCL |
12 |
NC |
|
| |
NC |
6 |
MOSI |
SDA |
11 |
NC |
|
| |
NC |
7 |
3.3V |
5V |
10 |
5V |
power Supply |
| Ground |
GND |
8 |
GND |
GND |
9 |
GND |
Ground |
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label |
Name |
Default |
Description |
|---|
| LD1 |
PWR |
- |
Power LED Indicator |
| P1 |
Vref |
- |
The absolute maximum rating of VREF supply voltage is 5V. The usage range is 0 to 4V. |
| SUPPLY |
PWR |
- |
The absolute maximum rating of VM supply voltage is 50V (no active). The usage range is 4.5 to 44V. |
DC Motor 14 Click electrical specifications
| Description |
Min |
Typ |
Max |
Unit |
|---|
| Supply Voltage |
4.5 |
5 |
5.5 |
V |
| VM Power Supply |
4.5 |
- |
45.0 |
V |
| Maximum Output Current |
0 |
- |
3.5 |
A |
| Operating Temperature Range |
-40 |
- |
85 |
°C |
| Logic input (VIN(L)) |
0 |
- |
0.8 |
V |
| Logic input (VIN(H)) |
2.0 |
5 |
5.5 |
V |
| VREF |
0 |
- |
4.0 |
V |
| Power dissipation |
- |
2.85 |
- |
W |
Software Support
We provide a library for the DC Motor 14 Click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
The library covers all the necessary functions to control DC Motor 14 click board. DC Motor 14 click communicates with the target board through the AN and RST lines on MikroBUS. This library offers functions for setting or clearing of both pins used for communication, also user can use functions that drive motor forward and in reverse or apply brake and stop functions.
Key functions:
void dcmotor14_forward ( ); - Function is used to drive the motor forward.void dcmotor14_reverse ( ); - Function is used to drive the motor reverse.void dcmotor14_brake ( ); - Function is used to brake the motor.
Examples description
The application is composed of three sections :
- System Initialization - Initializes LOG structure and sets AN and RST pins as output.
- Application Initialization - Initializes GPIO driver and starts log.
- Application Task - This example demonstrates the use of DC Motor 14 click by driving it forward motion for 5 seconds, than applying brakes it for 2 second, and then driving it in reverse for 5 seconds, after that, it stops for 2 second.
void application_task ( )
{
mikrobus_logWrite( "The motor turns forward!", _LOG_LINE );
dcmotor14_forward( );
Delay_ms( 5000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( "The motor brakes!", _LOG_LINE );
dcmotor14_brake( );
Delay_ms( 2000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( "The motor turns in reverse", _LOG_LINE );
dcmotor14_reverse( );
Delay_ms( 5000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( "The motor stops", _LOG_LINE );
dcmotor14_stop( );
Delay_ms( 2000 );
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This Click board™ is supported with mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Resources
Downloads

